Receding Gums
Written By Sharon Boyd, RDH, BS. | Reviewed by Lara T. Coseo, DDS
What are Receding Gums
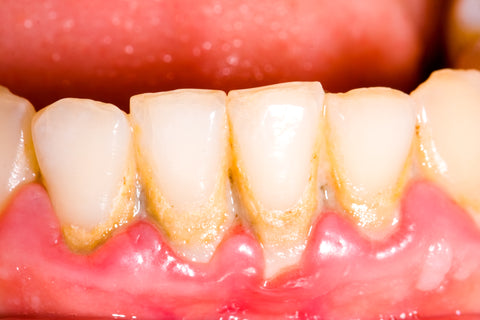
What are receding gums? Receding gums are gums that have pulled away from the surface of the tooth and crept away, exposing the root of the tooth. There are several different causes for receding gums that can result in sensitivity or even tooth loss. Because the gums help support the teeth, receding gums should not be taken lightly.
Causes of Receding Gums
There are a number of causes for receding gums. The most common is gum disease. Gum recession is usually due to one of the following causes:
Gum Disease
When you suffer from gum disease, there is an active infection under the surface of your gums between them and your teeth. These germs are attacked by antibodies in your bloodstream, which creates inflammation, redness and destruction of the fibers that attach the gums to your teeth. As gum infections persist, the gums creep farther down the root surface due to destruction of attachment fibers.
Abrasive Tooth brushing
Using a medium or hard-bristled toothbrush can cause more harm than good. Aggressive brushing – even with a soft-bristled brush – is traumatic to your gum tissue and can cause or advance existing gum recession.1
Brushing too aggressively is an easy fix. It is important to remember that your gums are made of a soft, sensitive tissue that is easily damaged when it is brushed too harshly. You may consider switching to a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush in a gentle and circular motion. However, if you use an electronic toothbrush just allow it to do the work and do not try using it like a traditional toothbrush. The additional motion is too aggressive on your gums.
Buildup Of Harmful Germs
The buildup of harmful germs in the mouth can be a bit more difficult to control. Regardless of what you do you will always have germs in your mouth. Saliva is a natural defense mechanism built in for fighting these germs. The saliva is very rich in oxygen and full of important enzymes that fight the harmful germs in your mouth. The downside is that the effectiveness of the saliva is altered by the food you eat, the regiment you follow when brushing your teeth, and the oral care products that you use.
Tobacco Use
Smoking makes it very difficult to manage gum recession and promotes loss of gum attachment. However, the use of smokeless tobacco is the most harmful method of tobacco use when it comes to receding gums.2 The abrasive ingredients inside of smokeless tobacco cause irritation to the tissue and are typically associated with severe gum recession in the area where the tobacco is most often held.
Tooth Misalignment
Crowded, misaligned teeth are at an increased risk to have gum recession. This may be to excess force placed on them during oral hygiene, or it may be due to anatomical forces that encourage the loss of gums and bone around these teeth.
Grinding Of The Teeth
If you suffer from clenching or tooth grinding, your teeth tend to flex along the neck of the tooth, near the gumlines. This is typically seen as an abrasion in the tooth enamel, but it may also contribute to loss of gum attachment in areas where enamel is damaged.
Orthodontic Therapy
Teeth that are moved too rapidly may not allow proper reformation and transition of the supporting tissues around the affected teeth.3 This often results in unnatural bone loss around those teeth, followed by gum recession around the affected tooth. It may also cause destruction of the roots.
Oral Anatomy
There are also situations where the structure of the mouth in general can make someone predisposed to receding gums. If the layer of bone around a newly formed tooth isn't thick enough then the gum tissue that forms around it will be thinner as well. This can make it more fragile and not able to withstand the normal forces that are applied to it from chewing food and proper brushing.
If you’ve ever noticed the small strip of skin between your lower lip and your two front middle teeth, you should know that this frenum might also contribute to recession in certain cases. Rarely, the frenum may be exceptionally tight or short, causing increased stress on the attached tissue on the tooth. As a result this may pull over time and cause the gums to recede due to the tension.
Signs And Symptoms of Receding Gums
One thing that separates this condition from other conditions of gum disease is how easy it is to diagnose. Many times other variations of gum disease go on unnoticed because there is no pain or visible difference associated with them. When faced with receding gums you can visibly tell that something is wrong. You will also notice that your teeth are more sensitive to touch and to food or drinks that are hot and cold. This is a result of the gum recession exposing the root of the tooth.
Receding gums can really sneak up on you if you are not careful. Typically gum recession is a very slow process that may not be noticeable at first, until you begin to see the roots of the teeth. Your dentist measures gum recession in millimeters and even two millimeters of attachment loss is significant. Here are some typical signs that you may be suffering from receded gums
Sensitivity
When you have receded gums, a portion of the root is exposed to outside elements. They were not meant to be exposed and often respond with hypersensitivity. Even simple toothbrushing along the gumlines can cause an intense pain that feels as if the nerve has been exposed.
Sensitivity is due to the exposed pores on the root surfaces. These pores have nerve endings that extend from inside of the tooth to the outside of the tooth. When gums recede, stimulation can reach the pores and send jolting signals toward the nerve.
Exposed Root Surfaces
The portion of tooth anatomy that is under enamel is called dentin. Dentin appears yellow next to the white tooth enamel and is exposed when the gums recede. When you see this yellow area next to a defined white crown, you will know that recession has occurred.
Redness And Swelling
If your gum recession is related to gum disease or periodontitis, there will be some inflammation and swelling associated with the area of gum recession. When plaque biofilm, tartar and other germs thrive near and under the gumlines, the body’s natural response is to destroy the attachment of the gums in the area. This causes infection and receding gums.
Teeth That Appear Longer Than Normal
When gums recede, the root of the tooth is exposed between the dental crown and the gumlines. The result is the appearance of a long tooth. Only one tooth may appear long or your entire smile may seem to be made up of long teeth. This appearance is due to receded gums.
Spaces Between Teeth
The appearance of dark spaces between your teeth near the gumlines is due to the loss of the gum “papilla” between the teeth. As gums recede, this sharp point of gum tissue is lost, as it creeps away with the other supporting gum tissue. The result is dark spaces between the teeth that were formerly covered with gum tissue.
Food Packing
As the gums recede and cause spaces between the teeth to be exposed, food easily becomes packed and lodged in these areas. Typically you will find one or more particular spaces that food packs in the majority of the time. Naturally these areas should be covered by gums and prevent food from lodging in the space. When food packs in problem areas it tends to compound and cause a consistent area of irritation and infection when not completely removed. This leads to further gum recession.
Association With Gum Disease
Food packs between the teeth but especially in the gum pockets that are formed beneath the gumlines against the teeth. As gums recede it also causes less tissue to be attached to the root of the tooth. Gums with natural healthy pockets measure up to two or three millimeters deep. As gums become diseased and lose attachment, the pockets become deeper. If you have gum recession that measures a significant five or six millimeters, it can be very serious because even with an area of no infection there will be an additional two to three millimeters of unattached gums within the pocket. If infection does exist, the pocket could be four millimeters or deeper. When combined with deep gum disease pockets, gum recession can be very serious and evidence of possible future tooth loss.
Stages of Receding Gums

Recession is measured by the distance between the margin of your crown (where the enamel tapers off, called the cementoenamel junction) and the level of the gums.
Gum recession is measured in the following categories:
- Class I – Mild gum recession. There is no bone loss or loss of tissue between the teeth.
- Class II – Gum recession extends toward the border of attached and loose gingiva. There is no bone loss or loss of tissue between the teeth.
- Class III – Gum recession extends past the border of attached and loose gingiva. Bone loss or loss of tissue between the teeth is evident. The root is partially covered.
- Class IV – Severe gum recession that is associated with gross loss of bone. There is no root coverage.
Receded gums are measured in terms of attachment loss. Simply having mild gum recession does not mean you are in the clear for gum disease. You may have mild recession with just one to two millimeters of exposed root surface, but a very deep pocket under the gumlines that is symptomatic of severe periodontitis. However, severe gum recession also means there obviously cannot be enough bone support on that portion of the tooth, meaning tooth stability is at risk. The more moderate to severe your gum recession, the more susceptible your tooth is to mobility and loss.
Dangers And Health Risks
Gum recession is a key factor in maintaining healthy tooth stability. Losing attachment levels around a tooth can ultimately lead to tooth loss, which also affects the adjacent teeth in the area. If recession is due to habits such as abrasive brushing, grinding, clenching or tobacco use, it is important to halt these before even more loss can occur.
Receded gums can also be a signal that you are suffering from gum disease. Healthy gums are tightly attached to the teeth near the margin of the dental crown, with no exposed root surfaces. If inflammation, bleeding, redness or sore gums are associated with your receded gums, it is likely that you are suffering from periodontitis. This severe form of gum disease is directly associated with health risks and conditions45 such as:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Respiratory disease
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Erectile dysfunction
- Preterm labor
- Premature and underweight babies
Gum recession may be slow, or it may be very progressive. Most recession is usually noticed when you have already lost two millimeters of attachment around the tooth, leaving a mild amount of root surface exposed. The more severe your gum disease, the quicker you will see the attachment levels being lost. If the cause of your recession is due to grinding or abrasive brushing, the signals may take longer to appear. Any signs of recession during orthodontic treatment should immediately be brought to the attention of your orthodontist. Recession during orthodontic therapy is a sign that movement is occurring at too rapid of a rate, with gum and bone levels not being able to keep up with the repositioning.
How To Prevent Receding Gums

Keep Gum Disease In Check
Treating early signs of gum disease like bleeding and sore gums will keep recession at bay. Neglecting gum health allows periodontitis to occur, which causes gums to detach from the surfaces of teeth. As a result, gum recession occurs and is directly linked with stability of teeth with periodontitis infections. The best prevention plan is to use a daily oral hygiene program that includes brushing, flossing, and rinsing. Use 100% pure botanical oral hygiene products that kill the bad germs that lead to gum problems
The best way to prevent receding gums is to pay close attention to they types of food you eat and by making sure that you use an effective oral hygiene regiment daily. The best oral hygiene plan includes flossing your teeth in the morning and evening, brushing your teeth after you floss, and using a mouthwash or rinse.
Use A Soft-Bristled Toothbrush
A common cause of receded gums is from brushing too hard or brushing with a medium or stiff-bristled toothbrush. Not only do stiff bristles cause gum recession, but they can also abrade – wear down or rub away by friction -the enamel away from the tooth.
Brush with a soft-bristled brush and only place as much pressure as needed to cause gentle tissue blanching. Anything more forceful is damaging to your gums and can push them away from the teeth.
Wear A Guard During Nighttime Grinding
If you wake up with sore jaws, or have sharply worn teeth, you may be grinding or clenching your teeth together. Because this action also causes the teeth to flex and break near the margin of the gums, you may suffer gum recession as a side effect. Preventing flexing and wear associated with teeth grinding can reduce the risks of gum recession.
Check Your Gums Regularly
During your normal oral care time, look in the mirror to see if there are any abnormal gumlines. Your gums should appear fairly even with one another (considering the scalloped pattern along your teeth). If you have one or more teeth that appear longer than the same tooth in the opposite side of the mouth, it may be suffering from recession. Ensure you are following proper oral care methods and treat gum infections appropriately to ensure the condition does not worsen.
Treatments for Receding Gums
Conventional Treatments
In order to fix receding gums, conventional treatment requires surgical measures. Most surgery for receding gums is invasive and uncomfortable, requiring lengthy healing times. In order to surgically treat receding gums, tissue is typically taken from another location and then placed in the area needed in order to repair receding gums. Gum grafting can be a fairly expensive procedure, averaging several hundred dollars for a single tooth. Typically multiple teeth are just a small additional charge.
An unfortunate truth about receding gums is that they are not thought about from the preventative standpoint. Typically people do not do research on them until something is really wrong. Several clinical studies have shown that no product is available that will help gums grow back once they've receded. If you already have this condition then you need to take preventative measures. Do what you can to keep your gums from worsening and concentrate on keeping your mouth healthy and clean to avoid further complications. Receding gums can lead to very costly dental procedures that could be required to keep your teeth.
There are different types of graft surgery used to treat receding gums.
Tissue Grafts
Traditional graft surgery involves tissue taken from the roof of your mouth and then sewn into place (sutured – joining two edges together) where the gum recession has occurred, covering the exposed root surfaces.
Pedicle Grafts
When there is enough excess tissue around the area of gum recession, it may be possible to have a small incision made, creating a flap. This flap is then stretched across the area of the gum recession and sewn (sutured) into place.
Donor Tissue Grafts
Tissue may also be used from a tissue bank. Using donor tissue results in less healing time because there is no need to remove or make incisions to access graft tissue within your own mouth. The donor tissue is sewn (sutured) into place or held in place by an additional protein additive.
Frenectomy
The small flap of skin that extends from between the middle of your lower front two teeth and the lip is called a frenum. If the frenum is too tight it can cause the gums to pull away from the teeth. For areas that suffer gum recession due to a tight frenum, simply snipping the frenum can reduce the stress that it placed on the gum margin. A frenectomy usually costs no more than a few hundred dollars, but typically needs to be paired up with a graft surgery for the affected area.
Natural And Home Remedies
Holistic Dental Options
The use of herbal supplements and remedies can create a healthier oral environment that promotes gum attachment levels. Many essential oils can be used on a toothbrush or in a glass of water to use as a mouthrinse.
Home Remedy Options
When you’re trying to reverse receding gums, the important part is to know how to stop receding gums. There are natural options available that can promote oral health by aiding in the destruction of harmful germs and creating an overall healthier environment that promotes gum attachment.
Remedies for receding gums truly lie within great oral hygiene practices that are gentle on the gums. Using gentle, 100% pure products along with a daily oral hygiene program can help fight harmful oral germs, the cause behind many gum problems.
Lifestyle Recommendations And Changes

Give Up Tobacco
Tobacco is one of the worst external factors when it comes to reversing oral disease conditions. The use of tobacco is harmful to the health of the gums and in most cases prevents the healing process from occurring. In cases of gum recession, smokeless tobacco is especially harmful as it causes direct tissue irritation and can further gum recession into very severe states
Limit Your Sugar And Acidic Foods
If you suffer from symptoms of gum disease, eating a diet that consists of processed foods, refined sugars, acidic drinks and alcohol can create an environment that allows germs to thrive. Eating a balanced diet free of sugars and acids is extremely beneficial to tissue health and reducing live disease germs in infected areas.
Reduce Stress
Stress is a common cause of teeth grinding and clenching. Consider making choices that help limit stressors and participate in relaxation techniques such as yoga. The use of an appliance during sleep may also help prevent excess strain due to muscle tension.
Your Questions About Receding Gums Answered
Why are my gums receding? Gums recede for several different reasons. The primary cause of gum recession is due to gum disease. When germs invade the area around the tooth it causes the gums to detach and creep farther down the root. Other causes include the use of tobacco, abrasive toothbrushing techniques, tooth misalignment and grinding.
Do receding gums grow back? Receding gums do not grow back. However, lost gum tissue can reconnect in the area of the gingival pocket 'the pocket below the gums next to the tooth'. This can prevent further gum recession. Gum tissue can only reattach if the area is healthy and free of gum disease.
How can I reverse receding gums? If receding gums are due to gum disease, treating the gum infection will halt the progression of the gum loss. In most cases you cannot re-grow gum tissue on your own. It is important to stop gum recession before it progresses to the point where you need surgical gum grafting. You can encourage gum reattachment in areas of gum disease by reversing the disease and keeping the tissue healthy.
Can I repair receding gums naturally? If your gum recession is due to gum disease it is possible to help reverse the gum infection. Unfortunately gums do not typically repair themselves. It is best to treat the condition by stopping whatever is causing it and then seek professional help for advanced stages of gum recession. If gums have simply lost connection to the tooth, this gum pocket can be repaired through treating the gum disease and creating a healthy environment for the tooth.
What are the common causes of receding gums? Common causes of receding gums are:
- Gum disease
- Tobacco use
- Abrasive toothbrushing
- Misaligned teeth
- Grinding
- Orthodontic treatment
My gums are only receding on one tooth. Why is this? Some teeth are more susceptible to recession than others. If you have a tooth that is out of alignment (such as due to severe crowding) or in an area where you scrub harder during brushing, this typically happens near the corners of the mouth, then those teeth may be more likely to suffer from receding gums.
Could I be making my gum recession worse? Yes. Brushing the area too hard or using too stiff of a toothbrush can actually cause your gums to recede even more. Only use a soft-bristled brush and apply just enough pressure where the tissue begins to blanch. Overaggressive brushing can cause more recession as well as enamel abrasion. Likewise, delaying treatment or using tobacco products can encourage the advancement of receding gums.
What will happen if my gum recession isn’t treated? If gum recession is allowed to progress, it causes a lack of support around your affected tooth. When tooth support is compromised, the tooth can become loose or mobile. Over time this mobility typically results in loss of the tooth due to its inability to firmly stay in the socket.
How can I be proactive with receding gums? The most important thing to do if you're suffering from receding gums is to take action that will prevent it from worsening. This means not only sticking to a strict oral hygiene plan but also adjusting it so you do not cause more physical damage. At this point it becomes more important to brush more gently and use a mouth rinse that will get to the places where harmful germs grow to stop them from multiplying. Most commercial mouthwashes are loaded with chemical additives that can dry the mouth inherently increasing germs growth.
How did my receding gums start? There are a lot of different reasons why people get receding gums. Common causes include periodontitis, gum disease, bruxism, clenching and grinding, overzealous brushing, habits, or using a stiff toothbrush. In some cases, rapid tooth movement from orthodontic therapy can also lead to recession. People who smoke or use tobacco products also experience high rates of receding gums.
What should I have done to keep from getting receding gums? Usually the most important step in preventing gum recession is to reverse gingivitis when it first starts. If you see signs of bleeding or swollen gums, improve your oral hygiene before it progresses into periodontitis.
How can I stop receding gums right now? Focus on cleaning your gumlines twice per day, using a soft toothbrush and floss. It’s important to clean the margin thoroughly. Supplementing with antiseptic mouthwash or essential oils after brushing and flossing can help to stall inflammation and the germs responsible for gum disease. Book a cleaning twice per year to have calcified buildup removed by your dentist or hygienist.
How can I improve my receding gums? Unfortunately, there is no way to improve an area affected by gum recession on your own. The key is to prevent it from getting worse. If the receding gums are severe, there are treatments you can get from your dentist to improve or cover it.
Can you restore the receded gums? Your dentist can perform procedures like a gingival graft or pinhole gum rejuvenation to physically cover the exposed root surface with new gum tissues. Sadly, it’s not possible for gums to grow back without professional intervention.
Can receding gums heal on their own? Will my receding gums regrow? No, they cannot. Which is why it’s extremely important to intervene the moment you suspect receding gums, gingivitis, or have symptoms of periodontal disease. But you can have your dentist treat the area with surgery or a graft to re-cover the part of your tooth that is exposed.
Will receding gums regenerate? No. Gingival tissues are extremely sensitive and cannot regenerate in a way that re-grows them over the roots of your teeth.
What do receding gums look like? Typical gums will have a scalloped shape that follows the contour of your tooth 'crown', which is the portion fully covered by enamel that extends above a normal gumline. If the gums recede, a portion of the root will be exposed. You will usually be able to see where the enamel crown tapers off to meet a more yellow-colored root. At that point the gumlines will be uneven and further down your teeth.
Can I fix receding gums without surgery? You can treat the cause of gum recession which is usually gum disease or aggressive brushing to prevent it from getting worse, but it is not possible to fix receding gums without the help of a dentist. Your dentist will need to perform a minor surgery to repair the tissue loss.
Do receding gums hurt? Not usually, unless the gums are inflamed from a periodontal infection. Gums that are receding because of harsh brushing will typically feel the same as any of the other gums in your mouth. However - exposed tooth roots do tend to be more sensitive, which could lead to pain when eating, drinking, or breathing in cool air.
What do receding gums feel like? Receding gums leave the underlying root exposed to the outside elements. Although the gums will feel the same as others, you will be able to feel the rougher and more sensitive portion of your tooth (which is not covered by protective enamel.) That part of your mouth will also probably be more sensitive.
Do gums recede with your age? Long in the teeth or long toothed used to be terms used when you were referring to people who were more advanced in their age. While gum recession can progress over time, it is not necessarily caused by aging but rather your oral care habits and dental health.
Are receding gums a bad thing? Mild gum recession does pose its own challenges such as increased risk of tooth decay and sensitivity but moderate to severe receding gums could jeopardize your smile as a whole, resulting in tooth loss.
Are receding gums serious? Yes. Your gums cover the supportive bone that hold your teeth intact. If you have receding gums, it also means that the bone underneath is shrinking away. Untreated gum recession is linked to periodontal disease, which can impact your overall health.
Are receding gums dangerous? If your gum recession is a side effect of periodontal 'gum' disease, then yes. Inflammation and germ infections inside of your mouth can statistically increase your risk of health problems like pneumonia, diabetes, heart attack, and stroke. There are studies that show a direct correlation between the severity of gum disease and numerous underlying medical conditions, including infertility and erectile dysfunction.
When should I worry about receding gums? As soon as you start to notice gum recession, it’s time to do something about it. Improve your oral hygiene routine, treat your gums delicately by not brushing too hard, and talk to your dentist about getting screened for periodontal disease.
Are receding gums genetic? No. However, if your gum recession is caused by periodontal disease, it is possible to pass the germs responsible for the infection by sharing food or kissing. Oral hygiene habits tend to be passed on in households, which is why some people say gum problems run in their family.
Are they hereditary? No. If your parents had gum recession, it does not mean that you will have them as well. However, you may be more prone to receding gums because of the same oral hygiene practices. Anatomical characteristics where specific teeth are out of line (which may be hereditary) could also lead to an increased risk of recession in those parts of your mouth.
Is receding gums normal? Although receding gums are a common thing to see in a dental office, they are not healthy or considered to be normal. They’re the result of something going wrong inside of your mouth, be it trauma or disease. Gum recession affects almost half of adults.
Are they common? Yes. Since most people don’t know that brushing too hard can cause recession, or that the receding gums are a result of their gum disease, it’s common to see this condition in about 40% of adults (and 70% of seniors.)
Do receding gums cause bad breath? Receding gums aren’t the cause of bad breath. But, if gum disease is the source of your recession, it can also cause halitosis alongside of your other dental problems.
Can receding gums lead to tooth loss? Yes. When your gums recede, it means there is less gingiva and bone structure left to secure your teeth in place. Eventually the teeth will become mobile or fall out. Your dentist will need to use a periodontal probe and take X-rays to measure the extent of bone loss around your teeth.
Does it cause teeth to fall out? It can, if it’s severe enough. If your recession is the result of gum disease, it’s not just receding gums that you need to worry about; you should be just as concerned with the bone height underneath your gums! Extensive bone loss can lead to teeth falling out or needing to be extracted.
Why are my gums receding? Gums usually recede because of periodontal disease, harsh toothbrushing, tobacco use, or orthodontic treatment. However, they’re also associated with misaligned teeth, clenching and grinding, traumatic injuries, or habits like picking at your teeth.
What are receding gums a sign of? Any time you see your gums starting to recede, it means that there’s a deterioration of the support structures that hold your teeth in place. It could be a sign of either disease or trauma, so you need to have it examined by your dentist as soon as you notice the symptoms.
Are receding gums permanent? Unless your dentist repairs the area with a graft or 'pinhole' surgery, then yes, the gum recession is permanent and may possibly even get worse.
Can I recover from receding gums? While it’s possible to stop the cause of your gum recession, you cannot recover or grown back the gums. However, dental procedures such as gingival grafting and gum rejuvenation can re-cover the part of your tooth that has been exposed.
Can receding gums be filled? Sometimes gum recession is mild enough that you may prefer for your dentist to put a filling (dental bonding) over the part of the root that’s exposed. Doing so improves aesthetics and minimizes tooth sensitivity. The only way to fill in the lost gingiva with new gums is to perform a graft or to have surrounding tissues stretched over the area that’s exposed.
I have receding gums – what should I do first/Immediately? Evaluate your brushing and flossing routine. Are you brushing too hard? Using a hard toothbrush? If so, switch to a soft or extra-soft bristled brush and only use just enough pressure to see light blanching in your gums. But if you notice swelling, redness, and bleeding when you floss, you need to book a dental exam right away.
Do receding gums bleed? They will if your recession is caused by gum disease. Usually they won’t bleed if it’s the result of overzealous brushing. Your gums will only bleed if there’s an active infection, such as gingivitis or periodontal disease.
Does receding gums mean gum disease? It can. Gum disease and aggressive toothbrushing are the leading causes of gum recession, so it’s important to determine the source so that you can treat your gum recession properly.
Is receding gums the same thing as gingivitis? No. Gingivitis is mild inflammation along the edges of your gums, due to plaque buildup and poor oral hygiene. If gingivitis is not corrected, it can progress into gum disease which does cause gum recession.
Are receding gums a disease? They are one of the numerous symptoms of gum disease, but periodontal infections are not the only cause of recession.
Is it periodontal disease? There is about a 50/50 chance that your gum recession is the result of periodontal disease. If you’re experiencing bleeding gums, bad breath, tartar buildup, or tooth mobility, then you need to see your dentist about getting screened for periodontitis.
Are receding gums a sign of cancer? Not usually. However, gum recession is common in people who use tobacco products both cigarettes and smokeless tobacco' which can increase your chance of developing oral cancer.
Are receding gums a sign of mouth cancer? Mouth cancer from tobacco use may accompany tobacco-induced gum recession.
What is the best electric toothbrush to use for receding gums? Switching to an electric toothbrush can be useful if you tend to be heavy handed. Select a style of brush head with soft or extra-soft bristles. Usually the cheaper economy brushes have harder/stiffer bristles. Hold the brush in place and allow it to do the work on its own.
Can receding gums cause jaw pain? When the roots of your teeth are exposed such as in moderate to severe cases of gum recession it can increase your risk of tooth hypersensitivity, which in turn may radiate pain throughout other areas of your mouth when you eat and drink.
Are receding gums normal if you wear braces? Sometimes, yes. If the teeth are quite misaligned or being moved too quickly, gum recession may be evident.
Can you get receding gums while pregnant? Most pregnancy-induced gingivitis cases involve swelling and bleeding along the gumlines, but not gum recession. Symptoms typically improve with home care, professional cleanings, and after giving birth when your hormone levels stabilize.
Do receding gums mean I will have bone loss? Yes. Any time we see the gums starting to recede around a tooth, it means that the supporting bone underneath the tissues has also shrunk away.
Can you get receding gums from dipping tobacco? Yes. The small irritants inside of dip/snuff improve uptake of the nicotine but are harsh on gum tissues. Repeatedly holding snuff or dip in your mouth will gradually cause the gingiva to recede. In addition to giving up tobacco, it is recommended that you rotate the dip instead of holding it in the same part of your mouth each time you use it.
Do receding gums require surgery? Sometimes, yes. A graft or pinhole surgery can help to position new gingiva or stretch surrounding gums over the area of your tooth that is exposed. Gum surgery protects your tooth roots, lowers the risk of sensitivity and tooth decay, limits additional recession, and improves aesthetics.
Does receding gums cause a throbbing pain? When the roots of your teeth are exposed because of gum recession, it can cause mild to severe tooth hypersensitivity. It is especially noticeable when eating foods that are cool or cold.
Can receding gums cause facial numbness? No. If you are experiencing facial numbness seek immediate medical attention.
Are receding gums a permanent problem? Without professional intervention, preventative techniques, improved oral hygiene, and possible gum grafting or pinhole surgery, recession can be permanent.
Do gums recede quickly? Recession occurs at varying rates, depending on the cause. Aggressive brushing and gum disease tend to cause gradual gum recession, while tobacco use or orthodontic-induced recession may be quicker to develop.
References:
-
1Litonjua, L.A., Andreana, S.; Bush, P.J., Cohen, R.E.; “Toothbrushing And Gingival Recession.” Int. Dent. J. April 2003. 53(2):67-72.
-
2National Cancer Institute. “Smokeless Tobacco: Health And Other Effects.” Web 4 Dec. 2012.
-
3Dilsiz, A.; Aydin, T.; “Gingival Recession Associated With Orthodontic Treatment And Root Coverage.” J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2010;2(1):c30-3.
-
4Jepsen S, Kebschull M, Deschner J.; Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. {Relationship Between Periodontitis And Systemic Diseases}.{Article in German} 2011 Sep;54(9):1089-96
-
5Zuo Z, Jiang J, Jiang R, Chen F, Liu J, Yang H, Cheng Y.; Effect Of Periodontitis On Erectile Function And Its Possible Mechanism.; J Sex Med. 2011 Sep;8(9):2598-605.
|
Article Written By Sharon Boyd Sharon has been a Registered Dental Hygienist since 2001. She also holds a Bachelor of Science degree in Human Relations and Business. In 2011, she began implementing her dental knowledge into freelance writing services that aided dentists, product designers, continuing education providers and web marketing firms for their online and distribution purposes. She has since bridged her services into the medical and cosmetic surgery fields. |
 Article Reviewed by Dr. Lara Coseo Article Reviewed by Dr. Lara CoseoLara T. Coseo, DDS, is a 2004 graduate of Baylor College of Dentistry. She has 13 years of experience practicing general dentistry. She currently serves as a part-time faculty instructor at Texas A&M College of Dentistry and writes dental website content and blog material. |





